RFID Application: Smart Management Solution in Logistics and Production
RFID applications are increasingly being deployed in many fields, from warehouse management to smart transportation. Thanks to the ability to quickly identify and retrieve data, this technology helps optimize operating processes and improve management efficiency. This article will analyze in detail the outstanding RFID applications and future development trends!
What is RFID?
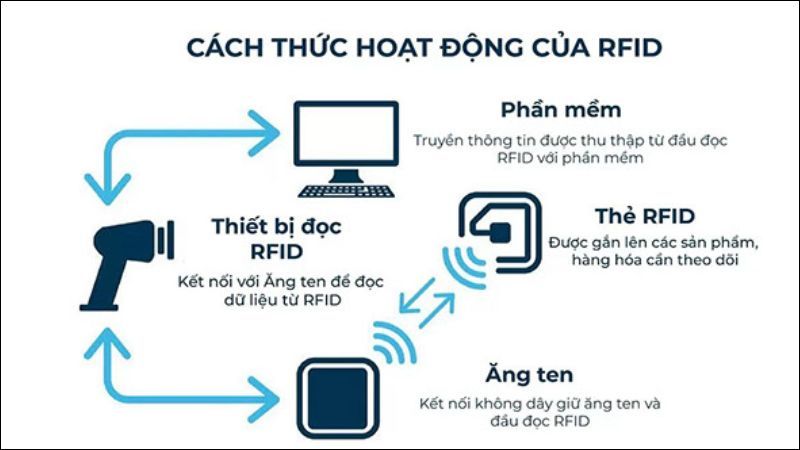
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a radio frequency identification technology that allows data transmission between RFID tags and RFID readers without direct contact. The special feature of RFID lies in its ability to automatically identify, quickly process and store information in real time.
Compared to traditional barcodes, RFID has advantages in scanning speed, the ability to read multiple objects at the same time and high accuracy even when the tag is obscured. This makes the technology the foundation for many modern management systems.
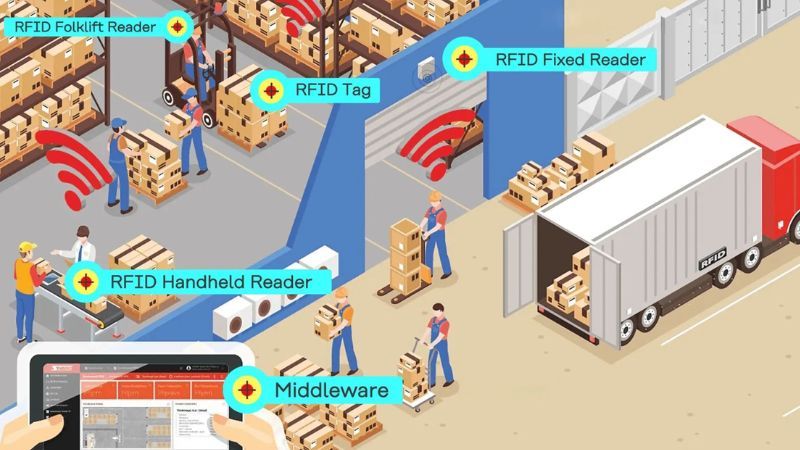
Outstanding practical applications
1. Asset tracking and inventory management
One of the most common RFID applications is asset management and inventory tracking. Each product or device tagged with RFID helps businesses:
- Know the exact quantity of inventory.
- Track product location in real time.\
- Reduce loss and errors in inventory.
This is especially useful for industries with large quantities of goods such as retail, logistics, supermarkets or industrial manufacturing.
2. Access control systems and libraries
RFID technology is also used to manage security and building access. Instead of using traditional keys, employees only need to swipe RFID cards to open the door. The system will automatically record the time and identity of the person entering and exiting.
In the library field, RFID supports automatic borrowing and returning of books, helping to reduce queuing time, while limiting the loss or misplacement of books.
3. Application in intelligent transportation (ETC)
One of the clear examples of RFID application in life is the non-stop toll collection system (ETC) on highways.
Vehicles only need to attach an RFID tag, when passing through the toll station, the system will automatically deduct money from the account without stopping. This technology helps reduce congestion, save time, and at the same time, make toll management more transparent.
4. RFID in logistics and supply chain
In logistics, RFID plays an important role in optimizing transportation and controlling the flow of goods. When each package is tagged, businesses can easily track the transportation process from the warehouse to the customer.
This helps:
- Reduce the loss of goods.
- Optimize the delivery process.
- Support the analysis of supply chain data to predict demand and manage inventory.
5. Applications in the fashion and retail industry
In the fashion and retail industry, RFID is used to manage inventory and shopping experiences. For example:
- Attach RFID chips to clothes and shoes for quick inventory.
Integrate into smart anti-theft systems.
Personalize the customer experience, when the system can suggest related products based on shopping habits.
Thanks to RFID, major brands can optimize operations, reduce losses and increase business efficiency.
Benefits and challenges when implementing
1. Advantages: speed, accuracy, contactless, automation
RFID applications help increase data processing speed, reduce errors compared to manual input. The system operates without direct contact, convenient in many environments such as warehouses, transportation or retail. In addition, RFID supports automation of management processes, saving manpower and improving efficiency.
2. Challenges: investment costs, security, data management
In addition to the advantages, RFID applications also pose challenges. The initial investment costs are quite high, especially for small businesses. Security issues and the risk of RFID card copying also need to be noted. In addition, when deploying on a large scale, managing and synchronizing the volume of RFID data requires appropriate technology infrastructure.
Trends and future of RFID
1. Integrating RFID with IoT, AI and smart systems
In the future, RFID applications will be associated with IoT and AI to form smart systems. Information collected from RFID can be automatically analyzed, supporting inventory forecasting, transportation coordination or real-time security control.
2. New applications: attendance, health care, behavior recognition
In addition to logistics or transportation, RFID is gradually expanding to other fields. In education, RFID helps with automatic attendance. In healthcare, RFID supports tracking patients, drugs and equipment. RFID is even being studied to identify consumer behavior, serve marketing and optimize experiences.
Conclusion
RFID applications have proven to play an important role in asset management, logistics and many other fields. Thanks to its fast and accurate identification capabilities, RFID helps businesses save costs and improve operational efficiency. It can be said that RFID applications are an important foundation for moving towards smart management in the digital age.